One of the most interesting things about beam splitter microscope imaging systems is that both the objectives for illumination in sensing systems and optical inspection and surface imaging are the same. So, what exactly are beam splitter microscope imaging systems and what are their applications?
Beam Splitter Microscope Imaging Systems
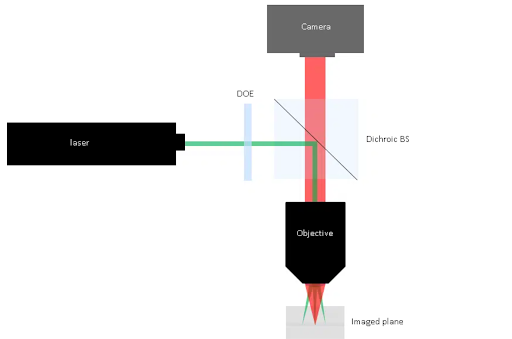
The beam splitter microscope setup is useful for several optical systems for a variety of applications, such as cytometry, defect analysis, and wafer inspection. The optical systems that use this setup consist of two arms that share the same focus optics.
- One arm of the optical system known as the illumination arm involves the shaping of laser light , followed by the beam traversing through the objective to reach the surface and form an image.
- The other arm is called the imaging arm which involves collecting the light scattered from the surface . In this arm, other optics are used together with the objective to collect fluorescence-induced illumination.
A dichroic beam splitter window or cube, or any similar beam splitter optics can be useful to combine these two arms.
Diffractive Beam Shapers and Diffractive Beam Splitters
A diffractive beam shaper can shape an incident laser beam and transform the beam into various geometrical shapes, such as rectangle, line, and round shapes with flat-top intensity. Therefore, in case of small feature detection, diffractive beam shapers are efficient as parts of the illumination arm.
Diffractive beam splitters consist of optical transmissive and diffractive optical elements. These optical elements use the principle of diffraction to generate several discrete output beams by splitting an input laser beam. The most exciting thing about diffractive beam splitters is that they can generate a variety of different arrays of spots, such as huge 2-dimensional arrays of spots with uniform intensity and equal separations.
In the case of challenging applications like cytometry, wafer inspection or STED where the detection has to be highly accurate, a manufacturer can customize the diffractive beam splitters to produce any specific laser spot with a particular position, number, and intensity.
Integrating Diffractive Optics in Beam Splitter Microscope Systems
An ideal setup for beam splitter microscope systems places the diffractive optical element in front of the dichroic beam splitter. We don’t need to bother about the positioning of the DOE as they produce the same pattern for different positions.
Applications
In the microscopy setups, laser beam splitters have several common applications, such as
- Beam splitters can function as a live distance gauge by producing a grid or line of spots. Because of their excellent angular accuracy, diffractive beam splitters are particularly efficient for this application.
- Beam splitters can form an array of Gaussian depletion spots and an array of donut-shaped spots. This is why beam splitters are useful for large field of view STED.
Beam shapers, on the other hand, have many applications in flat top round field illumination and flat top line generation. From industrial wafer inspection to life science, beam splitter microscope systems have a long list of applications. However, it is important to properly place the DOE on the illumination arm to develop an effective beam splitter microscopy system.
Keep an eye for more latest news & updates on Tech Sky!